A decision-making tool for countries to implement the Multilateral System of Access and Benefit Sharing

Many countries seek assistance in developing the necessary institutional, legal, policy and administrative mechanisms to implement the Plant Treaty’s Multilateral System. To support countries, Bioversity International and partners have developed a new decision-making tool.
The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (Plant Treaty or ITPGRFA) is one of the most important achievements of the international community in the last decades. It recognizes the crucial importance of plant genetic resources for ensuring food and nutrition security, and puts in place mechanisms that facilitate international cooperation for the conservation, exchange and sustainable use of crop and forage diversity, and for sharing benefits derived from the use of those resources. Among these mechanisms, the Plant Treaty’s Multilateral System of Access and Benefit Sharing creates a virtual pool of plant genetic resources available at no cost for research, breeding and training activities in all countries that are parties to the Treaty.
The national and regional implementation of the Multilateral System requires extensive capacity building at different policy and administrative levels. Many countries that are Contracting Parties to the Plant Treaty seek assistance in developing the necessary institutional, legal, policy and administrative measures or mechanisms. The FAO/Bioversity/ITPGRFA Secretariat Joint Capacity Building Programme for Developing Countries on Implementation of the ITPGRFA and its Multilateral System of Access and Benefit Sharing (Joint Capacity Building Programme) has been designed and implemented to respond to some of those requests for assistance, based on priorities established by the Plant Treaty’s Governing Body.
The most recent product of the Joint Capacity Building Programme is a decision-making tool for national implementation of the Multilateral System published by Bioversity International.
The tool is designed to assist national-level policy actors to identify appropriate measures to implement the Multilateral System within their country, taking into consideration the fact that a growing number of countries that are Contracting Parties to the Plant Treaty are also parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity's Nagoya Protocol* on access and benefit sharing. The tool is based on experiences gained working with national partners in a number of countries over the past eight years developing national policies and systems to implement the Multilateral System, and in particular under the Bioversity-led ‘Genetic Resources Policy Initiative’ and the project for Mutually supportive implementation of the Plant Treaty and the Nagoya Protocol in Benin and Madagascar.
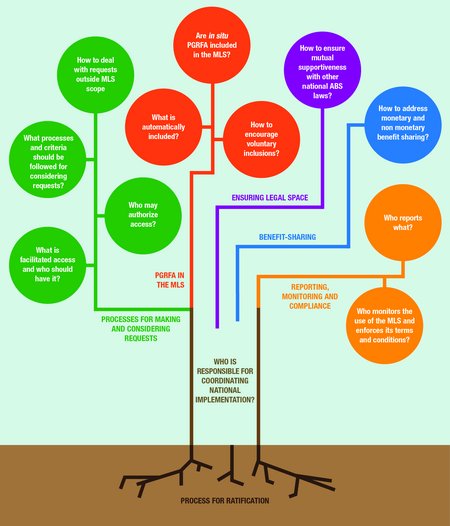
The decision-making tool is divided into eleven sections corresponding to issues that national-level policy actors need to address:
- Who is responsible for promoting and coordinating national implementation?
- What is facilitated access to plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA) under the Multilateral System and who has the right to facilitated access?
- Who may authorize access to PGRFA under the Multilateral System?
- What processes and criteria should be followed to consider requests for PGRFA included in the Multilateral System?
- How to deal with requests for purposes that are (or may be) beyond the scope of the Multilateral System?
- What PGRFA are automatically included in the Multilateral System?
- How to encourage voluntary inclusions by natural and legal persons?
- How to ensure legal space for the implementation of the Multilateral System?
- How to address benefit sharing?
- How to deal with reporting obligations regarding transfers and sales?
- Who monitors the use of PGRFA under the Multilateral System and enforces the Multilateral System’s terms and conditions?
Each section is presented in a question-and-answer format. Among other things, each section considers:
- If there are means of simultaneously implementing other parts of the Plant Treaty, for example conservation (Article 5), sustainable use (Article 6), farmers' rights (Article 9) or the global information system (article 17)
- If there are important issues to consider related to the mutually supportive implementation of the Nagoya Protocol on access and benefit sharing
- If it is useful, given the legal and political culture of the country concerned, to develop new policies or laws to implement the Multilateral System (which underscores that many countries are implementing the Multilateral System without creating new laws).
At the end of each section, draft ‘baseline’ legal provisions are provided. They can be adapted and incorporated into new laws and administrative guides, if and when they are considered to be useful.
Download the decision-making tool (available in four languages)
Arabic | English | French | Spanish
Interested users can request hard copies of the tool to Bioversity International by sending an email to Evelyn Clancy
*The Nagoya Protocol is an international agreement to the 1992 UN Convention on Biological Diversity to ensure that benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources are shared in a fair and equitable way.
The Joint Capacity Building Programme has collaborated with various national and international organizations and independent experts to develop the tool. They include the ABS Capacity Building Initiative, and the Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
The development of the tool was supported by the Ministry of Economic Affairs of the Netherlands, and is part of the CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) and the CGIAR Genebank Platform, which are supported by CGIAR Trust Fund Donors.