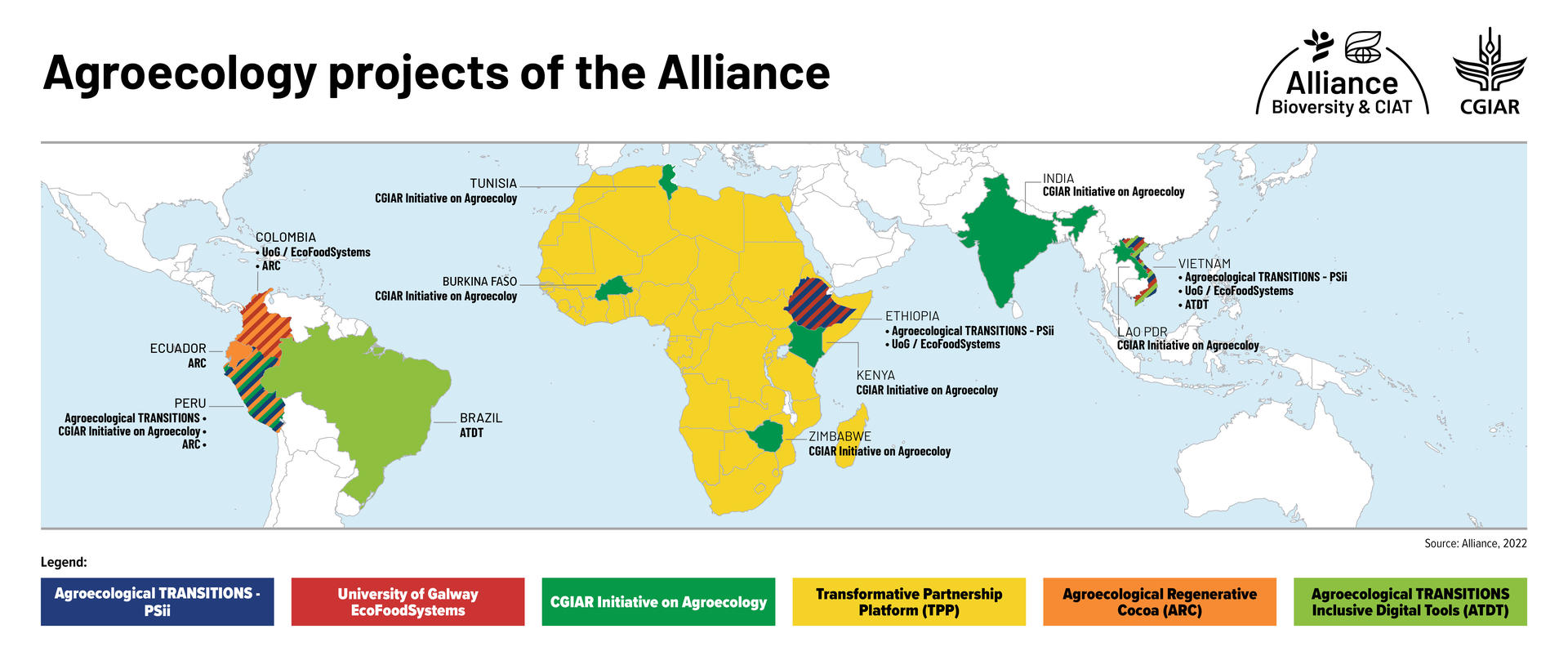
| Agroecology projects with the Alliance |
Alliance project coordinator |
Funder |
Duration |
Partners |
Countries |
Production systems wheat |
Level of engagement |
Below |
Project objectives/Work packages |
Link |
|
Agroecological TRANSITIONS – PSii
|
Jonathan Mockshell |
EU/IFAD |
2022-2025 |
Transformative Partnerships Platform (TPP) Agroecology;
HealthyFoods Africa;
Clima-Loca;
Sustainable Amazonian businesses; Sustainable Rice Platform |
Ethiopia
Vietnam
Peru |
Wheat
Rice
Cocoa |
Landscapes, Food Systems |
To enable agroecological transitions through the development and adoption of holistic metrics for food and agricultural systems performance, inclusive digital tools and transparent private sector engagement |
1. Improving private and private-public sector incentive models to support agroecological transitions for farmers and consumers.
2. Increasing transparency and traceability in supply chains on agroecological metrics and principles.
3. Enhancing the capacity of local institutions for engaging in private-public finance models, assessments and policies that support agroecological transitions.
|
Private Sector Incentives and Investments (PSii) for Climate change, resilience and environmental sustainability |
| University of Galway/ EcoFoodSystems |
Steven Prager |
EU/IFAD |
2022-2025 |
NUI Galway
The Alliance
Rikolto (Belgian NGO)
Wageningen University & Research (WUR) |
Ethiopia
Vietnam
Colombia
|
Multiple |
City regional food systems |
Develop a systems-based approach for agroecological transitions of food systems for improved health and nutrition, with corresponding decision-support tools and multi-stakeholder platforms to facilitate coordinated, landscape-scale transitions to navigate associated benefits and tradeoffs for both rural and urban communities within city region food systems |
1. Develop a systems and evidence-based approach for priority-setting and targeting of landscape, value chain, community and farm scale agroecological intensification interventions/innovations that enable socially-inclusive food system and nutrition transformations.
2. Co-create scaling strategies for agroecological innovations to enable City-Regional food systems transitions that improve sustainability, nutritional security and climate resilience in each country with relevant stakeholders
|
|
| OneCG Transformative Agroecology Initiative |
Marcela Quintero |
CGIAR |
2022-2024 |
Biovision
Agroecology TPP
GIZ
CIRAD
ICRAF/CIFOR
Bio-Hub Trust
Asociacion para el Desarollo del programa Biocacao
INERA
IRESA
ATAE
INRGREF
INRAT
L’Institut de l’Olivier |
Burkina Faso
India
Kenya
Lao PDR
Peru
Tunisia
Zimbabwe |
Multiple, including mixed crop-livestock, rice, home gardens, coffee and cocoa |
Agroecological Living Labs (ALLs) |
Contextually relevant agroecological principles applied by farmers and communities across a wide range of contexts and supported by other food system actors by 2024 |
Work package 1: Transdisciplinary co-creation of innovations in Agroecological Living Labs (ALLs)
Work package 2: Evidence-based agroecology assessments
Work package 3: Inclusive business models and financing strategies
Work package 4: Strengthening the policy- and institutional-enabling environment
Work package 5: Understanding and influencing agency and behavior change |
|
| Transformative Partnership Platform (TPP) - Agroecology Viability |
Marcela Quintero |
Government of France |
2021-2023 |
CGIAR
ICRAF
CIRAD
INRAE
IRD
FAO
UNEP
Biovision
SDC |
Africa |
Multiple, focusing on smallholder production systems |
Field to farm and household scales |
The overall objective of this call is to better understand the socio-economic viability of
agroecological practices and their livelihood system impacts across environmental and
demographic gradients in Africa |
To conduct a holistic evaluation including:
1. Quantitative and qualitative assessment of the labour required by agroecological practices.
2. Income (including returns to labour) and food security outcomes for households with contrasted access to: income sources (non-farm and off-farm), markets and policy
incentives.
3. Intra household levers and lock-ins (in terms of access to knowledge, land tenure, gender, risk aversion, religion and age equity).
4. The economic value of ecosystem services and disservices relevant to the location of the case studies |
|
| Agroecological Regenerative Cocoa (ARC) |
Yovita Ivanova |
French Facility for Global Environment |
2021-2025 |
The Alliance
ICRAF
Conservation International
French chocolate company
Farmers' organizations |
Peru Colombia Ecuador |
Cocoa Agroforestry |
Landscape to farm level |
The project aims to contribute to the creation of sustainable cocoa systems that provide livelihoods for farmers, conserve forests and create – through land restoration, rehabilitation and transformation – 600 hectares of cacao farms in Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. |
1. To develop an integrated farming vision, through agroforestry cocoa farming systems (SAF), which includes production aspects as much as production, soil restoration or landscape conservation;
2. To strengthen the infrastructure and skills of producers and their organizations throughout the cocoa value chain, from production to final commercialization;
3. To create and implement instruments for impact analysis and monitoring of productive landscapes in the project's area of influence through community governance;
4. To capitalize on experiences and lessons learned on sustainable agricultural practices and the conservation of biodiversity and forest ecosystems
|
Business researchers, farmers NGOs and governments team up for sustainable cacao in South America |
| Agroecological TRANSITIONS Inclusive Digital Tools (ATDT) |
Lini Wollenberg |
EU/ IFAD |
2022 - 2024 |
IRRI;
CIFOR-ICRAF;
Transformative Partnerships Platform (TPP)
|
Brazil
Vietnam
|
Livestock
Rice
|
Farmers to food systems |
To support more inclusive digital tools for farmer technical advisors and performance assessment to enable climate-informed agroecological transitions at scale for rice systems in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam and livestock landscapes in Pará and Mato Grosso States, Brazil, with lessons for major tools globally and the potential to reach at least one million farmers by 2024. |
1. Understand the role of digital tools in inclusive knowledge development for achieving climate-informed agroecology at large scales
2. Improve inclusive knowledge development in digital tools for technical advisories and farm performance assessment
3. Demonstrate the benefits that farmers can derive from using improved digital tools and their potential to generate large-scale impacts for climate-informed agroecology.
|
ATDT |